Navigating through the realms of taxation becomes unequivocally seamless with a thorough understanding of Tax Declaration Forms. These pivotal documents, essential for affirming your income and deductible amounts to the tax authorities, serve as a transparent ledger of your fiscal year. Dive into a world where different types and examples of these forms become your allies in adherence to tax regulations. Embark on a guided journey from comprehension to creation, ensuring your pathway in the financial labyrinth is not only compliant but astute.
What is a Tax Declaration Form? – Definition
A Tax Declaration Form is an official document that taxpayers use to disclose their income, expenses, deductions, and other pertinent financial information to the tax authorities. These printable form, mandated by the tax regulatory body within a jurisdiction, allows individuals and businesses to calculate their tax liability based on the provided financial data. It serves to affirm the accuracy and completeness of the information declared, ensuring that tax obligations are met in accordance with prevailing tax laws and regulations. This aids in maintaining a transparent and lawful fiscal environment.
What is the Meaning of the Tax Declaration Form?
The Tax Declaration Form serves as a formal communication between the taxpayer and the tax authorities, providing a structured means to report income, deductions, and other pertinent financial details within a specified tax period. It’s a critical document that facilitates the calculation of tax liabilities, ensuring taxpayers comply with their fiscal responsibilities and legal obligations. This form aids tax authorities in ascertaining the accuracy and veracity of a taxpayer’s financial disclosures, thereby, underpinning a transparent and equitable taxation system. Essentially, it is a tool for maintaining accountability and adherence to tax regulations.
What is the Best Sample Tax Declaration Form?
The notion of a best sample Tax Declaration Form can vary since sample tax forms and their requirements are heavily contingent on the specific tax laws and regulations of a particular country or state. However, an effective Tax Declaration Form often shares common elements that ensure comprehensive, accurate reporting of an individual’s or entity’s financial standings.
Here’s a generic breakdown of what might be included in a well-structured Tax Declaration Form:
Header
- Title: Clearly indicating that the document is a Tax Declaration Form.
- Tax Year: The specific year for which the taxes are being declared.
- Identification Details: Including Name, Address, Tax Identification Number, etc.
Income Section
- Total Annual Income: Including wages, dividends, and other income sources.
- Income Sources: Detailed breakdown of income, potentially categorized by type.
Deductions Section
- List of Deductions: Itemized deductions like mortgage interest, educational expenses, etc.
- Total Deductions: Aggregated sum of all deductions.
Tax Calculations
- Preliminary Tax Liability: Calculated by applying the applicable tax rate(s) to the taxable income.
- Credits: Applicable tax credits, if any.
- Net Tax Liability: Preliminary tax liability adjusted for credits and previous tax payments.
Declaration and Signature
- Declaration Statement: A statement where the taxpayer declares the accuracy and completeness of the information.
- Signature: Where the taxpayer and potentially a witness, sign.
Additional Sections
- Attachments: A section that details any required or attached supplementary documentation.
- Instructions: Detailed guidelines on how to fill out and submit the form.
- Due Date: Stating the submission deadline for the tax declaration.
This generalized layout may encapsulate the vital components of an effective Tax Declaration Form, ensuring that taxpayers provide all necessary details required for accurate tax calculation and compliance with tax laws. Always refer to your specific jurisdiction’s tax authority for precise, legitimate Tax Declaration Forms to ensure legal compliance and accurate reporting. You should also take a look at our Employee Declaration Form.
FREE 40+ Tax Declaration Forms in PDF
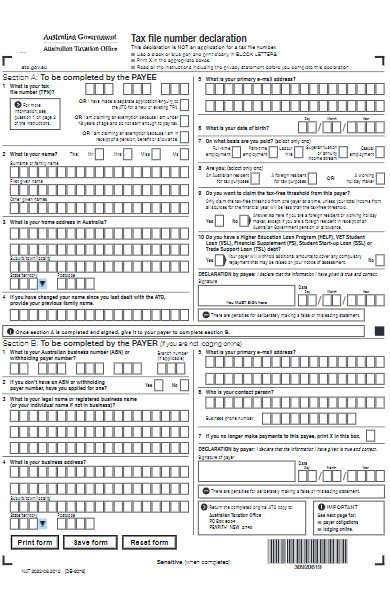
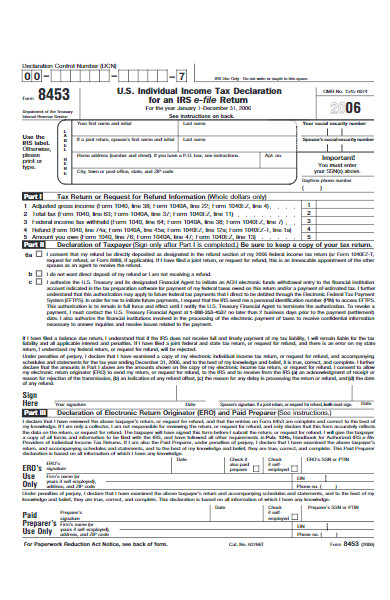
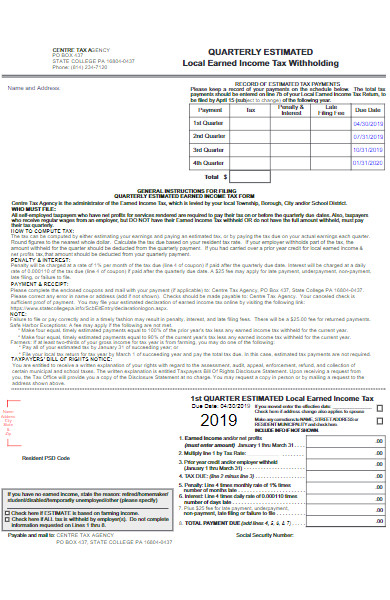
41. Agency Tax Declaration Form

What information is needed to complete a Tax Declaration Form?
Completing a Tax Declaration Form typically requires a thorough compilation of your financial details. While exact requirements might vary across different jurisdictions, the following pieces of information are generally necessary:
- Personal Information:
- Full name
- Address
- Social Security Number or Tax Identification Number
- Marital status
- Income Details:
- Total income from employment, businesses, or freelance work
- Investment income details, including dividends and interest income
- Any other additional income, such as rental income, royalties, or gains from the sale of assets
- Deductions:
- Details of deductible expenses, such as home mortgage interest, educational expenses, and medical costs
- Contributions to retirement accounts
- Charitable donations
- Tax Credits:
- Information related to eligibility for various tax credits like education credits, child tax credit, or energy credits
- Tax Payments:
- Total of taxes already paid through withholding or estimated tax payments
- Refund details if you’ve overpaid taxes during the year
- Dependent Information:
- Names, Social Security Numbers, and other relevant details of dependents
- Related expense details, such as childcare costs
- Business and Freelance Information:
- Total income and expenses if you’re a business owner or freelancer
- Details of business-related deductions, such as office expenses, travel, and depreciation
- Property Details:
- Information related to property ownership, property taxes paid, and income earned from property (if applicable)
- Foreign Income:
- Details regarding any income earned outside your home country
- Additional Financial Information:
- Details of any additional financial transactions that may impact your tax situation, such as inheritance, large gifts received or given, or participation in a high-value transaction
Always ensure that you refer to the specific form relevant to your jurisdiction and tax year, as requirements might change. When in doubt, consulting a tax professional or the local tax authority can provide clarity on the exact information needed for your Tax Declaration Form.
How do I properly fill out a Tax Declaration Form?
Filling out a Tax Declaration Form meticulously is crucial for accurate tax filing and compliance with fiscal responsibilities. Here’s a generalized step-by-step guide to assist you in this process. Please note that exact steps can vary, depending on your country and specific tax situation.
Step 1: Gather Necessary Documents
- Income Documents: Collect W-2s, 1099s, or other income statements.
- Deduction Information: Gather documents related to mortgage interest, tuition payments, medical bills, and charitable donations.
- Identification: Ensure you have Social Security Numbers for yourself (and spouse/dependents, if applicable).
Step 2: Choose the Right Form
- Determine which tax form is relevant to your situation (such as 1040, 1040EZ in the U.S., or respective forms in other countries).
Step 3: Fill Out Personal Information
- Clearly fill in your name, address, and other personal details.
- Provide information for dependents and spouse, if applicable.
Step 4: Report Your Income
- Accurately report all types of income: employment, investments, and others.
- Make sure to enter data in designated lines or sections accurately.
Step 5: Calculate Deductions and Credits
- Itemize deductions like home mortgage interest, educational costs, or select standard deduction as applicable.
- Calculate and claim eligible tax credits.
Step 6: Calculate Your Tax
- Use tax tables or computation worksheets to calculate the tax owed based on your taxable income.
- Subtract the tax credits from the tax owed.
Step 7: Factor in Payments
- Include all tax payments made during the year through withholding or estimated payments.
- Calculate the final tax due or refundable, considering the total payments made.
Step 8: Verify and Sign
- Thoroughly check all entries for accuracy.
- Ensure no section is left incomplete or inconsistent.
- Sign and date the form. If filing jointly, ensure your spouse also signs.
Step 9: Attach Required Documents
- Attach W-2s and other forms that document tax withheld.
- Include additional schedules or forms if required.
Step 10: Submit the Form
- Opt for e-filing or mail the form to the appropriate tax authority.
- Ensure timely submission before the tax filing deadline to avoid penalties.
Additional Tips:
- Consult a Professional: In complex tax situations, seeking assistance from a tax professional can be invaluable.
- Maintain Copies: Always keep copies of submitted forms and supporting documents for your records.
- Check for Confirmation: If e-filing, ensure you receive confirmation of submission from the tax authority.
Always adhere to the specific guidelines provided by your local tax authority or government when filling out your Tax Declaration Form. This guide is generalized and may not precisely represent your specific process.
What documents do I need to complete my Tax Declaration Form?
Completing a Tax Declaration Form requires thorough documentation to ensure accurate reporting of income, deductions, and credits. While the exact documents can vary by country and individual circumstances, here is a general list of documents that you might need:
Income Documentation:
- Salary Slips: Monthly income statements from your employer.
- Form W-2 or 1099: Documents that report your earnings and tax withholdings (U.S. specific).
- Investment Income Statements: Details of dividends, interest, and capital gains.
Deduction-Related Documents:
- Mortgage Statements: Detailing interest paid, for home mortgage interest deduction.
- Medical Bills: Outlining medical expenses that may be deductible.
- Tuition Fee Receipts: For claiming education-related deductions.
- Charitable Donation Receipts: Validating the amounts you contributed to charitable organizations.
Credit-Related Documents:
- Childcare Expense Receipts: For potential childcare credit.
- Educational Expense Details: Like student loan interest statements or receipts for tuition and books.
Personal Information:
- Social Security Numbers: For yourself, spouse, and any dependents.
- Bank Account Details: For direct deposit or withdrawal of tax refunds/payments.
Business or Self-Employment Records:
- Business Income: Records of income if you are a business owner or freelancer.
- Business Expenses: Including utility bills, rent, and supply costs for deductions.
- Vehicle Use: Mileage logs if using a vehicle for business purposes.
Property and Asset Documentation:
- Real Estate Documents: Property tax and rental income if you own real estate.
- Sales of Assets: Details of sales of assets like stocks or property.
Previous Tax Returns:
- Last Year’s Tax Return: To reference last year’s income, deductions, and credits.
International Income (if applicable):
- Foreign Income Statements: Records of income earned outside your resident country.
Special Circumstances:
- Unemployment Income: Statements of unemployment compensation received.
- Gambling Income: Records of any income from gambling or lottery winnings.
Additional:
- Energy Credits: Receipts for energy-efficient purchases or improvements.
- IRA Contributions: Statements of contributions to Individual Retirement Accounts.
Ensure to consult your country’s specific tax guidelines or a professional tax consultant to validate the documentation required as per your individual circumstances and applicable tax laws.
Where can I find and submit a Tax Declaration Form?
Navigating through the intricacies of finding and submitting a Tax Declaration Form can be complex and generally depends on the country in which you are filing taxes. However, here’s a broad guide to assist you:
Finding a Tax Declaration Form:
- Official Government Websites:
- Most countries have an official government website where you can download Tax Declaration Forms.
- Example: For U.S. citizens, forms can be found on the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website.
- Local Tax Offices:
- You may visit your local tax office to obtain a physical copy of the tax declaration form.
- Assistance and clarification on how to fill out forms may also be available here.
- Online Tax Filing Platforms:
- Numerous online platforms provide electronic versions of tax forms along with guided assistance in completing them.
- Examples include TurboTax, H&R Block, and other country-specific platforms.
- Tax Professionals:
- Tax consultants or CPAs often have access to all necessary tax forms and can provide them to you during your consultation.
- Libraries or Community Centers:
- In some regions, local libraries or community centers provide physical tax forms, especially during the tax filing season.
Submitting a Tax Declaration Form:
- E-Filing:
- Most countries encourage e-filing through the official government tax website or authorized e-filing platforms.
- You might need to create an account, input your information, and upload or fill out the tax form online.
- Mail:
- Some individuals prefer or may need to mail in their tax forms.
- Be sure to verify the correct mailing address from the official tax authority website, as different forms may have different mailing addresses.
- In-Person:
- Depending on your location, you might be able to submit your tax forms in person at a local tax office.
- Ensure to bring all necessary documentation and copies of the form for your records.
- Via a Tax Professional:
- If you’re working with a tax consultant or a CPA, they can often submit the tax forms on your behalf, either electronically or through mail.
- Using Tax Software:
- Utilize tax software platforms that allow you to fill and submit tax forms electronically.
- These platforms might also offer additional assistance in optimizing your tax return.
Remember to always verify deadlines for tax form submission and ensure that all submitted information is accurate to avoid any penalties or delays. Always refer to your country’s specific tax authority or a professional for precise and reliable advice. In addition, you should review our tax statement form.
Are there different types of Tax Declaration Forms for various income sources?
Yes, there are different types of Tax Declaration Forms tailored to various income sources and taxpayer categories, although the exact forms and their applicability can significantly vary depending on the country’s tax system. Here are some general examples:
- Personal Income Tax Form:
- For individuals to declare various income sources such as salary, freelance income, and investments.
- Business or Corporate Tax Form:
- Utilized by businesses to declare their income, deductions, and relevant financial activities.
- Capital Gains Tax Form:
- Often used to report income derived from the sale of assets like properties, stocks, or bonds.
- Self-Employment Tax Form:
- For freelancers, contractors, and other self-employed individuals to report their income and expenses.
- Rental Income Tax Form:
- For individuals or entities to declare income earned from renting out property.
- Investment Income Tax Form:
- To report income from various investments such as dividends, interests, and profits from financial market trading.
- Non-Resident Tax Form:
- Often required from non-residents who have earned income in the country.
- Gift and Inheritance Tax Form:
- Used to declare any substantial gifts or inheritances received which may be subject to taxation.
- VAT or Sales Tax Form:
- For businesses to report their collected sales tax or VAT.
- Withholding Tax Form:
- Employers often use this to report the amount of the employee’s income that was withheld for taxes.
Each of these forms typically requests specific information related to the income type and might allow for various deductions, credits, and adjustments based on the applicable tax laws. It’s imperative to select and complete the correct form to ensure accurate tax filing. Always refer to the tax authority website or consult a tax professional for accurate guidance relevant to your jurisdiction and individual circumstances.
Can I amend a Tax Declaration Form after submitting it?
Yes, in many jurisdictions, you can amend a Tax Declaration Form after it has been submitted, but the specific process, rules, and permissible time frames can vary widely depending on your location. Typically, tax authorities allow taxpayers to amend their filed tax returns if they realize they’ve made an error, omitted information, or encountered changes in their tax status. Here are some general steps and considerations, though specifics will depend on local regulations:
Steps to Amend a Tax Declaration Form:
- Identify Errors or Changes:
- Ensure that an amendment is necessary by checking the original submission against your records.
- Acquire the Correct Form:
- Obtain the appropriate amendment form from your tax authority—often labelled something similar to “Amended Tax Return”.
- Fill Out Accurately:
- Carefully fill out the form, correcting the errors or updating the relevant information.
- Include Additional Documentation:
- Attach any additional documents or information that supports the changes, such as revised financial statements or additional tax documents.
- Submit in a Timely Manner:
- Ensure that you submit the amended form within the allowed time frame, which may be dictated by tax laws or administrative rules.
- Track and Confirm:
- Keep copies of all documents and, if possible, track the submission to confirm it’s received and processed by the tax authority.
Considerations:
- Timing: Be aware of any deadlines for amending a tax return to ensure your changes are accepted.
- Penalties: Understand the implications of any errors or late submissions, such as potential penalties or additional tax due.
- Refunds: If you are amending a return due to an overpayment, check how and when you can expect to receive a refund.
- Additional Taxes: Be prepared to pay any additional taxes that may be due as a result of the amendment.
- State/Local Taxes: Remember that amending federal or national tax forms might also require changes to state, provincial, or local tax returns.
- Future Implications: Consider how changes might affect future tax returns and adjust your records and practices accordingly.
Always consult a tax professional or your tax authority’s guidelines to navigate the specifics of amending a tax return in your jurisdiction. Accurate and timely submissions are crucial to maintaining compliance and avoiding unnecessary penalties or scrutiny from tax officials. You may also be interested in our Custom Declaration Form.
How can I verify that my Tax Declaration Form has been received and processed?
Verifying that your Tax Declaration Form has been received and processed is essential to ensure that you are in compliance with tax regulations and to avoid any potential penalties. Here’s a general guide on how you might verify the receipt and processing of your Tax Declaration Form, keeping in mind that specific procedures might vary depending on your location and the tax authority in question:
1. Online Tax Portals
Many tax authorities provide online portals where taxpayers can:
- Check the Status: View the status of their tax submissions.
- Receive Notifications: Get updates or alerts related to their tax filing.
Steps to Check Online:
a. Log in to the online portal using your credentials. b. Navigate to the relevant section for checking the status of your submitted Tax Declaration Form. c. View the status, which might indicate whether it’s been received, is under review, has been processed, etc.
2. Email Confirmation
Some tax authorities send email confirmations upon receipt of online submissions.
- Check Your Email: Look for a confirmation receipt in your inbox or spam folder.
- Save the Confirmation: Keep the email for your records to have a timestamped confirmation of your submission.
3. Postal Mail
If you submit your form via postal mail, consider using a method that provides:
- Tracking: Use a postal service that allows you to track the delivery of your document.
- Confirmation: Opt for a service that provides a receipt upon delivery.
4. Direct Inquiries
- Phone: Some tax authorities offer helplines where you can inquire about the status of your submission.
- In-Person: Visiting a local tax office might be an option to check the status in person, if it’s permitted and safe to do so.
5. Consult Your Tax Advisor or Preparer
If you utilize a tax professional to handle your filings, they may have methods for confirming the receipt and processing of your documents.
6. Subsequent Communications
Pay attention to any subsequent communications from the tax authority, such as:
- Assessment Notice: Indicates that your declaration has been processed and assessed.
- Request for Additional Information: Might indicate that your form is being reviewed.
Additional Tips:
- Keep Copies: Always maintain copies of all documents submitted for your records.
- Note Submission Dates: Track when you submitted the form to be mindful of processing timelines.
- Follow Up: If the expected processing time has passed with no update, follow up with the tax authority.
Remember that the precise methods available for verifying the receipt and processing of tax forms will depend on the systems and practices of your local tax authority. Always adhere to their guidelines and use the resources they provide for accurate information regarding your tax filing.
Is it possible to fill and submit Tax Declaration Forms electronically?
Yes, in many jurisdictions, it is possible to fill out and submit Tax Declaration Forms electronically. This method of submission, often referred to as e-filing, has gained popularity due to its convenience and efficiency. Here’s a broad overview, noting that exact procedures can vary widely between different countries or even regions:
Advantages of Electronic Submission:
- Convenience: Allows you to file taxes from the comfort of your home or office.
- Speed: Electronic submissions are typically processed faster than paper forms.
- Security: Secure portals aim to protect your sensitive financial information.
- Documentation: Instant confirmation of submission and online tracking are often available.
General Steps to E-File Tax Declaration Forms:
- Registration:
- Create an account on the official tax portal of your jurisdiction.
- Verify your identity, often through email verification or through documents.
- Prepare Your Tax Declaration:
- Gather relevant financial documents, such as income statements, receipts, and other pertinent records.
- You may use online tools, software, or consult a tax professional to prepare your declaration accurately.
- Filling Out the Form:
- Log in to your account on the tax authority’s portal.
- Find the relevant tax declaration form and begin filling it out with the necessary information.
- Ensure all entered data is accurate to prevent any issues or delays.
- Document Attachment:
- Attach any required documents, such as proof of income, tax deductions, or credits.
- Ensure that documents are clear, legible, and in the permitted file formats.
- Review and Submit:
- Thoroughly review all entered information and attached documents for accuracy.
- Submit the form electronically through the portal.
- Payment:
- If you owe taxes, utilize the online payment options available, such as direct bank transfer, credit card, or other online payment methods.
- If you’re due for a refund, ensure your bank details are correctly entered for direct deposit (if applicable).
- Confirmation and Tracking:
- Upon submission, you should receive a confirmation, often via email or through the portal itself.
- Use tracking features (if available) to monitor the status of your submission.
Additional Points:
- Security: Ensure your internet connection is secure to protect your personal and financial information.
- Deadlines: Be mindful of tax filing deadlines to avoid penalties.
- Keep Records: Save all electronic confirmations and keep copies of all documents submitted.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure you comply with all tax laws and regulations pertinent to your jurisdiction.
Always refer to your local tax authority’s guidelines, as procedures, available forms, and permissible attachments may vary significantly.
How to Create a Tax Declaration Form?
Creating a Tax Declaration Form involves understanding taxation laws, financial data requirements, and maintaining clarity to ensure accurate data entry by the individual or entity declaring their income and deductions. Below is a generalized step-by-step guide. The actual process may vary widely based on your jurisdiction and specific tax law requirements:
Step 1: Understand Taxation Laws and Requirements
- Research Tax Laws: Understand income types, deductions, exemptions, and tax rates applicable in your jurisdiction.
- Consult a Professional: Tax professionals can provide insights into legal requirements and best practices.
Step 2: Define the Purpose and Use
- Identify User Group: Know whether the form is for individuals, businesses, or specific professions.
- Determine Use Cases: Identify scenarios in which the form will be used (e.g., annual tax filing, quarterly declarations, etc.)
Step 3: Structure of the Form
- Basic Information: Begin with sections for basic taxpayer information like name, tax ID, address, etc.
- Income Section: Include fields for various income types, such as salary, business income, and investment returns.
- Deductions and Credits: Include sections for applicable deductions and tax credits.
- Signature and Date: Ensure a space for validation, like a digital signature or manual signing.
Step 4: Ensure Clarity and Simplicity
- Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon and ensure instructions are straightforward.
- Logical Flow: Ensure the form flows logically from one section to the next.
- Provide Guidance: Where possible, include tooltips or links to guides on how to fill out the form.
Step 5: Maintain Compliance and Legal Consistency
- Adhere to Laws: Ensure the form complies with local, state, and federal tax laws.
- Validation: Include validation checks to minimize errors in data entry.
Step 6: Design and Layout
- Aesthetically Pleasing: Ensure the form is visually clear and organized.
- User-friendly Interface: If digital, ensure the form is easy to navigate and fill out.
Step 7: Data Security
- Secure Data Handling: Ensure that the form and any supporting system adhere to data protection regulations.
- Confidentiality Assurance: Provide information on how the data will be protected and used.
Step 8: Testing and Feedback
- Beta Testing: Have a sample group of users test the form for usability and clarity.
- Gather Feedback: Make necessary adjustments based on user feedback.
Step 9: Distribution and Accessibility
- Ensure Accessibility: Make the form easily accessible, both physically and digitally.
- Provide Support: Offer avenues for assistance in case users have questions or issues.
Step 10: Review and Update
- Periodic Review: Regularly review the form for continued compliance and usability.
- Update for Tax Law Changes: Ensure the form is updated to reflect any changes in tax law.
Always consult with a tax expert or legal counsel when creating a tax declaration form to ensure it meets all statutory requirements and adheres to all applicable laws. This guide is generalized and the actual process can be more complex based on specific needs and legal frameworks.
Tips for creating an Effective Tax Declaration Form
Creating an effective Tax Declaration Form requires a blend of legal compliance, clarity, simplicity, and user-friendliness to ensure that taxpayers can accurately and efficiently declare their incomes and deductions. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
1. Understand Tax Regulations:
- Stay Updated: Ensure that the form aligns with the most recent tax laws and regulations.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure that all elements of the form are legally compliant to avoid potential disputes.
2. Clarity is Key:
- Avoid Jargon: Use straightforward language that is easy to understand by all taxpayers.
- Clear Instructions: Provide concise and clear instructions on how each section should be completed.
3. Logical Structure and Flow:
- Sequential Ordering: Arrange sections in a logical order, guiding the taxpayer through the form.
- Categorization: Group related information together, such as personal details, income types, and deductions.
4. Accessibility:
- Multiple Formats: Make the form available in various formats, such as digital and paper, to cater to different preferences.
- Language Options: If possible, offer the form in multiple languages to cater to a diverse population.
5. User-Friendly Design:
- Legible Font: Ensure the form uses a clear, easy-to-read font.
- Adequate Spacing: Ensure there is enough space for users to fill in their details, especially in printed forms.
- Navigable Format: If digital, ensure users can easily navigate through different sections.
6. Data Security:
- Privacy Protection: Ensure the form adheres to data protection laws and communicates the security of personal information.
- Secure Channels: If available online, utilize secure, encrypted channels to protect submitted data.
7. Validation and Error Handling:
- Field Validation: If digital, implement validation checks to ensure data entered is accurate and complete.
- Error Messages: Clearly communicate any errors and guide the user on how to correct them.
8. Assistance and Support:
- Guidance: Provide tooltips or guidance notes within the form for additional help.
- Support Contacts: Include contact details for taxpayer support in case of queries or difficulties.
9. Testing:
- Usability Testing: Before rolling out, test the form with a diverse group of users and incorporate feedback.
- Consistency Checks: Ensure that the form consistently applies tax rules and calculations.
10. Revision and Updating:
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review the form for any necessary updates or improvements.
- Legislative Changes: Swiftly implement changes arising from alterations in tax laws or policies.
By focusing on a blend of compliance, clarity, and user-centric design, you can create a Tax Declaration Form that simplifies the tax-filing process for users while adhering to legal and regulatory obligations. Remember to consult tax professionals during the development to ensure accuracy and compliance.
A Tax Declaration Form is a pivotal document, enabling individuals and entities to disclose their income, calculate their tax liability, and claim permissible deductions. It’s imperative to comprehend its various types, adhere to its specified format, and follow guidelines for precise completion. Accurate and lawful creation ensures regulatory compliance, preventing legal repercussions and facilitating a transparent, accountable financial environment in governance and personal finance management. You may also be interested to browse through our other Business Declaration Forms.
Related Posts
31+ Evaluation Form
41+ Employee Evaluation Form
28+ Appraisal Form
FREE 14+ Joining Report Forms in PDF | MS Word
12+ HR Letter Form
20+ Personal Information Form
13+ Internal Audit Form
18+ Employee Information Form
14+ Cover Letter For Internship
14+ Leave Application Form
55+ Admission Form
12+ Car Sale Contract Form
14+Tenancy Agreement Form
15+ Summer Camp Registration Form
12+ Training Feedback Form