A Physical Assessment Form is a vital document used by healthcare professionals to evaluate a patient’s overall health. This form includes sections for vital signs, medical history, and physical examination findings. It helps in systematically recording important data, ensuring consistency and accuracy in patient care. Whether for clinical, school, or workplace assessments, using the right Assessment Form improves efficiency. Additionally, it aids in tracking health changes over time. The form supports healthcare providers in making informed decisions, and it complements other documentation like the Physical Form for medical clearance or routine checkups.
Download Physical Assessment Form Bundle
What is Physical Assessment Form?
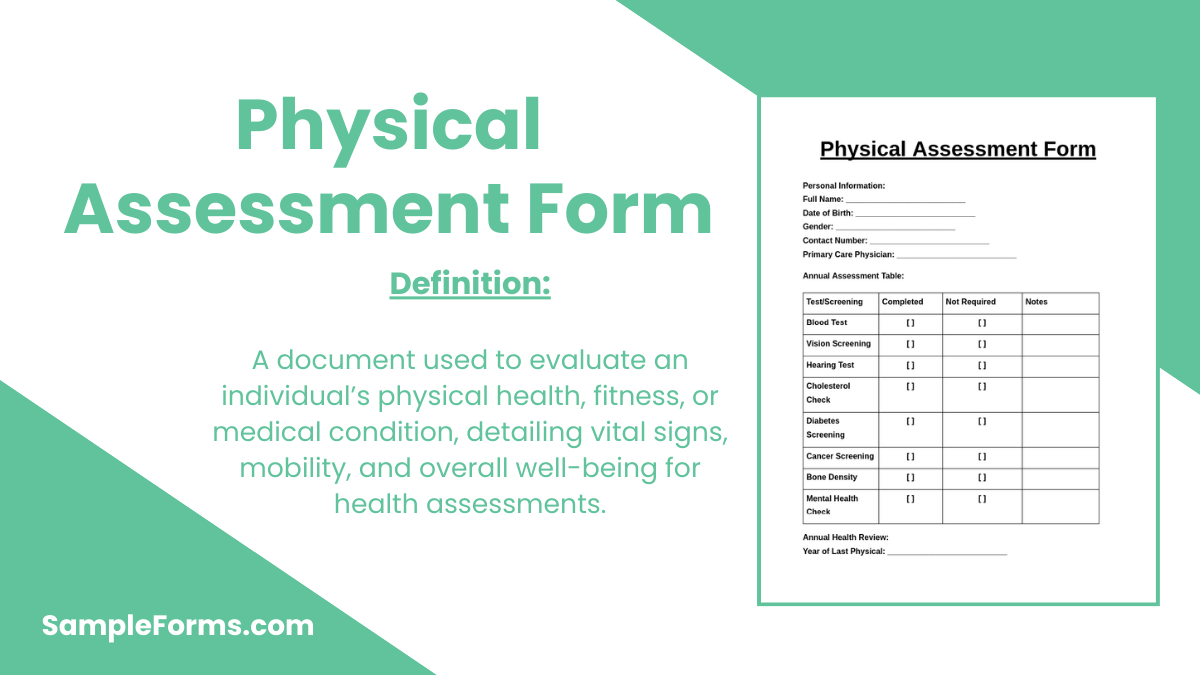
A Physical Assessment Form is a standardized document used to record a person’s health status through a comprehensive physical examination. It includes information such as vital signs, body system reviews, and medical history. This form ensures consistency in health evaluations and is commonly used in healthcare settings, sports, schools, and workplaces to monitor an individual’s well-being over time.
Physical Assessment Format
Personal Information:
Full Name: ___________________________
Date of Birth: ___________________________
Gender: ___________________________
Contact Number: ___________________________
Emergency Contact: ___________________________
Medical History:
Known Medical Conditions: ___________________________
Current Medications: ___________________________
Allergies: ___________________________
Previous Surgeries/Injuries: ___________________________
Vital Signs:
Height: ___________________________
Weight: ___________________________
Blood Pressure: ___________________________
Heart Rate: ___________________________
Temperature: ___________________________
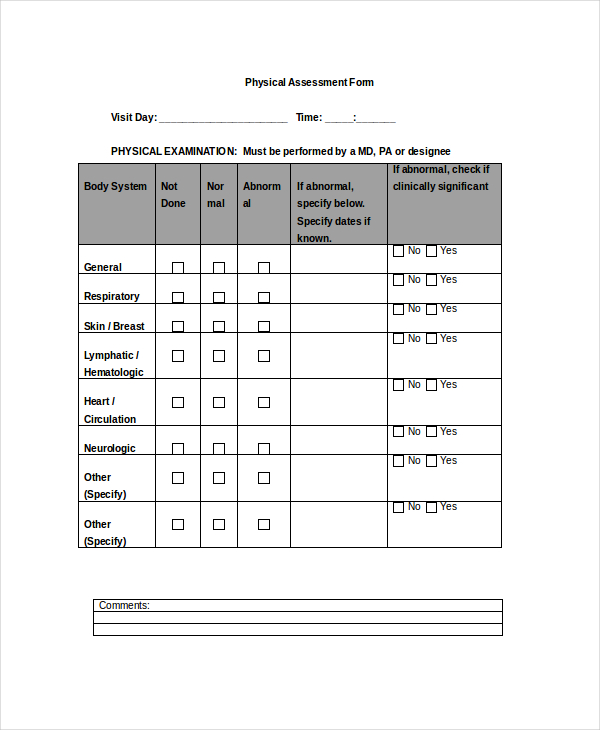
Physical Examination:
General Appearance: ___________________________
Respiratory Assessment: ___________________________
Cardiovascular Assessment: ___________________________
Musculoskeletal Assessment: ___________________________
Neurological Assessment: ___________________________
Assessment Summary:
Observations: ___________________________
Recommendations: ___________________________
Assessed By: ___________________________
Date: ___________________________
Physical Assessment Form for Healthcare Workers

A Physical Assessment Form for Healthcare Workers ensures the health and fitness of medical staff, detailing vital signs, medical history, and physical capabilities. Similar to an Interview Assessment Form, it evaluates fitness levels to maintain workplace safety and readiness.
Physical Assessment Form Nursing

The Physical Assessment Form Nursing helps nurses document patient health through comprehensive examinations, including vital signs, respiratory status, and cardiovascular health. Similar to a Physical Therapy Assessment Form, it aids in developing effective care plans based on clinical observations and patient needs.
New Patient Physical Assessment Form

A New Patient Physical Assessment Form gathers critical health information during the first medical visit. It records medical history, current medications, and vital signs, akin to a Nursing Assessment Form, ensuring personalized, accurate, and efficient patient care from the start.
Annual Physical Assessment Form
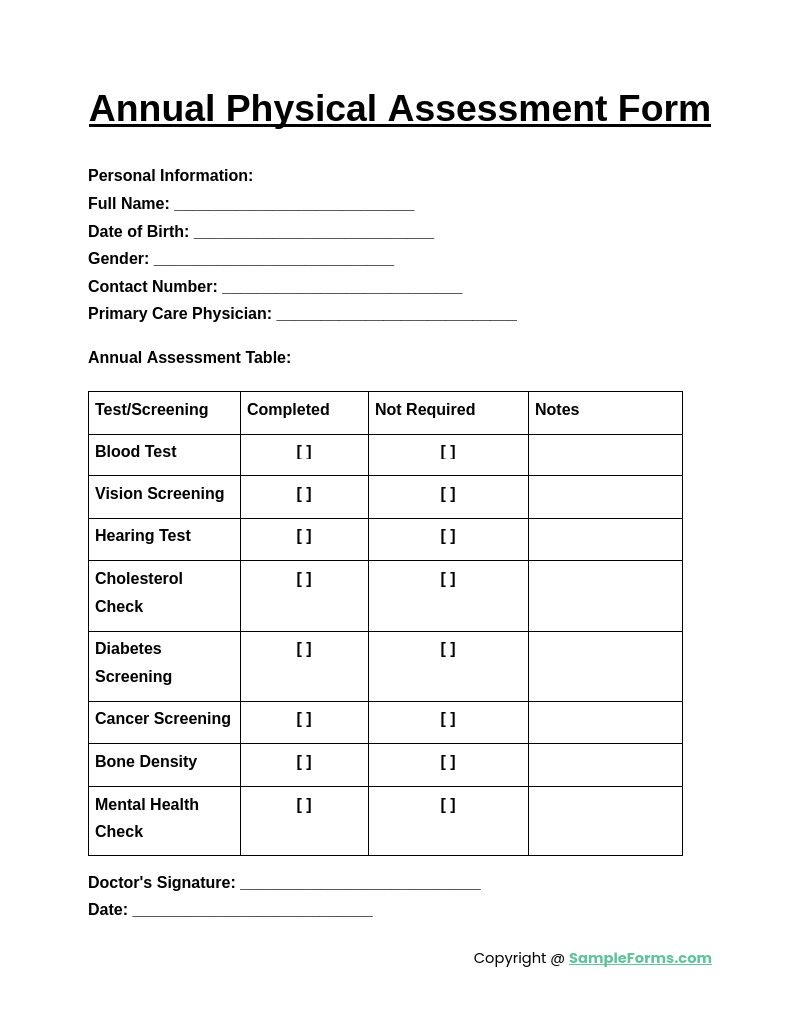
An Annual Physical Assessment Form is used for routine health checkups, tracking changes in a patient’s health over time. It includes sections for physical exams, immunizations, and lab results, much like a Fitness Assessment Form, focusing on preventive care and overall well-being.
Browse More Physical Assessment Forms
Health Care Practitioner Physical Assessment Form
Physical Fitness Assessment Form
MD Physical Assessment Form
Free Physical Assessment Form Download
Physical Assessment Checklist
Physical Assessment for Mental Health Patients Form
Physical Examination Form for Nursing Students
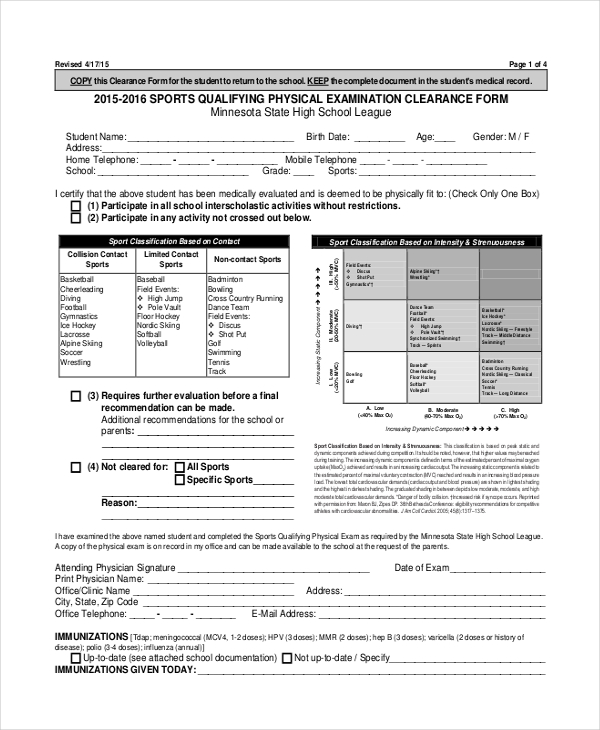
Sports Qualifying Physical Examination Form
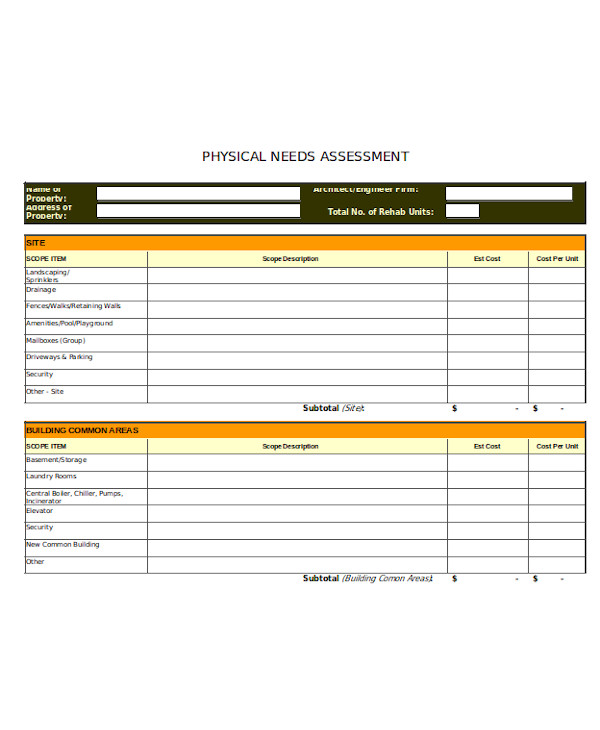
Physical Needs Assessment Form
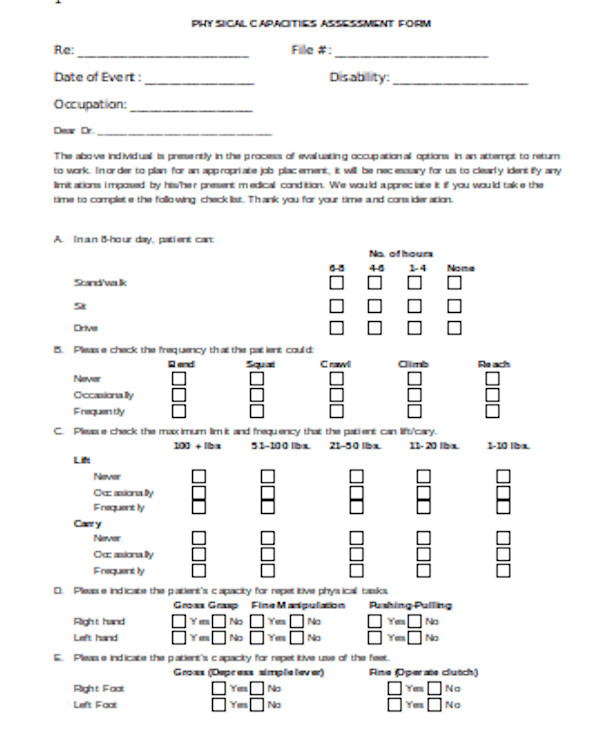
Physical Capacities Assessment Form
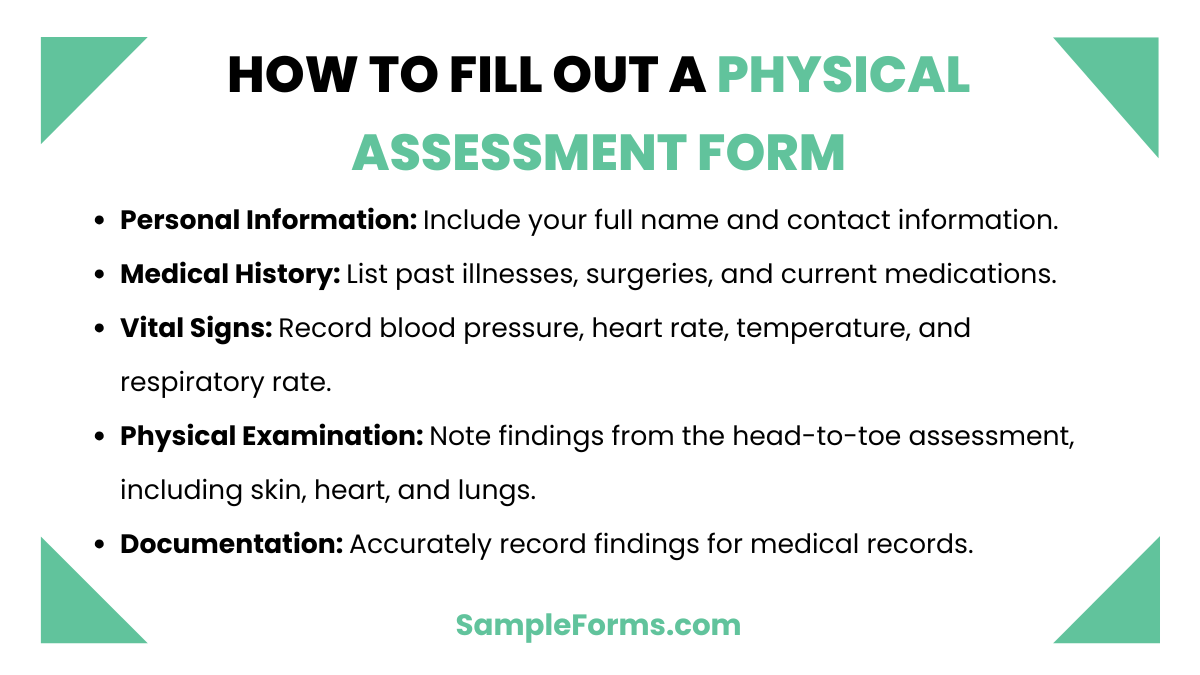
How do I fill out a physical assessment form?
Filling out a Physical Assessment Form involves accurately documenting personal health information, medical history, and current physical condition. Similar to a Nutrition Assessment Form, it helps evaluate overall health and well-being.
- Personal Information: Include your full name, date of birth, and contact information.
- Medical History: List past illnesses, surgeries, and current medications.
- Vital Signs: Record blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and respiratory rate.
- Physical Examination: Note findings from the head-to-toe assessment, including skin, heart, and lungs.
- Documentation: Accurately record findings for medical records.
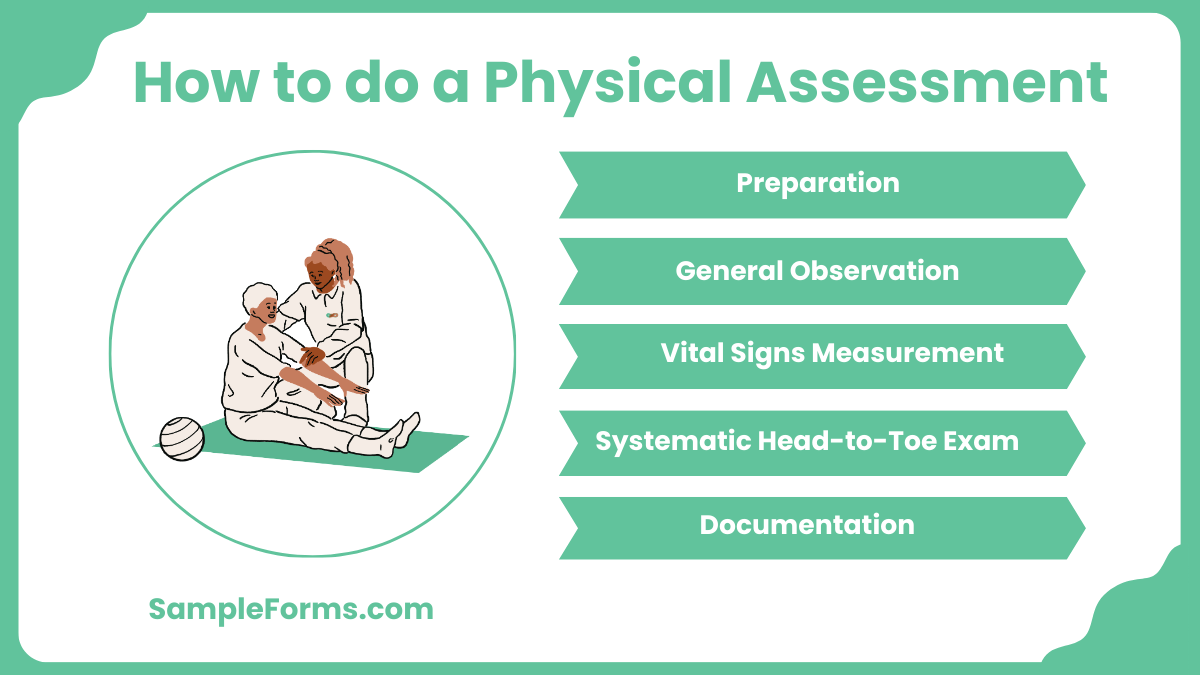
How to do a physical assessment?
A physical assessment evaluates a person’s overall health through observation, palpation, and diagnostic tools. Like a Mental Health Assessment Form, it identifies potential health issues.
- Preparation: Ensure privacy, proper lighting, and necessary equipment.
- General Observation: Assess appearance, posture, and behavior.
- Vital Signs Measurement: Record heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and respiration.
- Systematic Head-to-Toe Exam: Examine neurological, cardiovascular, respiratory, and musculoskeletal systems.
- Documentation: Accurately record findings for medical records.
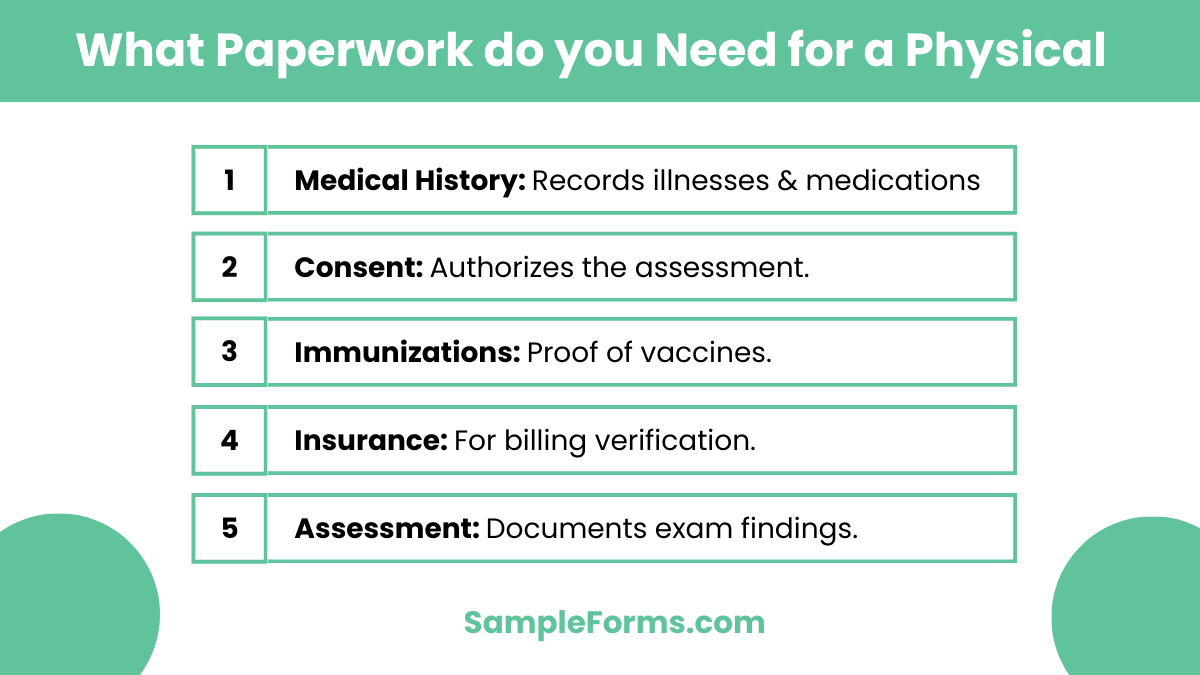
What paperwork do you need for a physical?
Paperwork for a physical includes forms that document medical history, current health status, and examination results. Similar to a Functional Behavior Assessment Form, it helps in understanding health patterns.
- Medical History Form: Details past illnesses, surgeries, and current medications.
- Consent Form: Authorizes the healthcare provider to perform the assessment.
- Immunization Records: Proof of vaccination history.
- Insurance Information: For billing and verification purposes.
- Assessment Form: To document physical exam findings.
What is a physical assessment for work?
A work-related physical assessment ensures employees meet job-specific health requirements. Similar to a Health Assessment Form, it evaluates fitness for duty.
- Pre-Employment Screening: Assesses general health before hiring.
- Job-Specific Tests: Evaluates physical demands related to the job.
- Vision and Hearing Tests: Required for safety-critical roles.
- Drug and Alcohol Screening: Ensures compliance with workplace policies.
- Documentation: A formal report for employer records.
What is included in a physical assessment?
A physical assessment includes a comprehensive health evaluation to detect potential health issues. Like a Skills Assessment Form, it systematically measures different health parameters.
- General Appearance: Observes physical condition, posture, and behavior.
- Vital Signs: Measures temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
- Physical Examination: Examines skin, heart, lungs, abdomen, and neurological responses.
- Medical History Review: Discusses personal and family medical history.
- Documentation: Records all findings for future medical reference.
How do I get a physical assessment?
Schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider. They’ll review your medical history, perform physical checks, and record results, similar to a Student Self Assessment Form.
Does a physical exam include a blood test?
Yes, many physical exams include blood tests to check cholesterol, glucose, and other health markers, often detailed in a Job Assessment Form.
How much does a physical exam cost?
The cost varies by provider and location, typically ranging from $50 to $200. Some expenses are covered by insurance, like a Supplier Assessment Form.
What is the first step in a physical assessment?
The first step is gathering medical history, including current symptoms, medications, and past conditions, similar to the process in a Vendor Assessment Form.
How to get a complete physical exam?
Book with your doctor, prepare health details, undergo vital checks, lab tests, and physical evaluations, as outlined in a Stress Risk Assessment Form.
How do I prepare for an assessment?
Get enough rest, stay hydrated, fast if required, and bring medical records—preparation steps often seen in a Property Assessment Form.
What should you not do before a physical exam?
Avoid caffeine, alcohol, heavy meals, or intense exercise before a physical exam. This ensures accurate results, like completing a Physical Exam Form.
What is a full body check-up called?
It’s commonly known as a comprehensive health screening or full physical exam, detailed similarly in a DOT Physical Form.
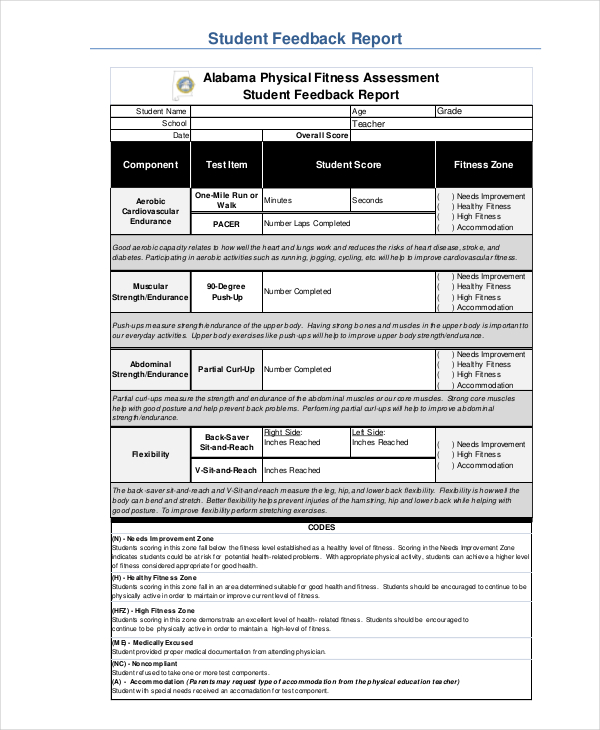
What is a physical fitness assessment?
A test measuring strength, endurance, flexibility, and cardiovascular health. Results are often documented in a Physical Report Form.
Are physicals not covered by insurance?
Many insurance plans cover annual physicals, especially preventive ones, like those required in an Employment Physical Form.
In conclusion, the Physical Assessment Form is essential for accurate health evaluations, promoting consistent documentation in medical, academic, and workplace settings. From routine checkups to specialized assessments, this form streamlines the process, ensuring comprehensive health tracking. Whether you need samples, templates, or guidance on creating effective forms, incorporating this document is key to organized and efficient healthcare practices. Additionally, it complements related documents like the Risk Assessment Form, helping identify and manage potential health issues effectively.
Related Posts
-
Content Retention Through Assessment Form [ How to, Importance, Tips ]
-
Enquiry Form
-
FREE 5+ Recruiter Performance Review Forms in PDF | MS Word
-
Job Safety Observation Form
-
FREE 4+ Hazard Observation Forms in PDF
-
FREE 5+ Coach Observation Forms in PDF | MS Word
-
FREE 4+ Child Care Observation Forms in MS Word | PDF
-
FREE 4+ Child Observation Forms in PDF | MS Word
-
Preschool Observation Form
-
Student Observation Form
-
Peer Observation Form
-
Lesson Observation Form
-
Assessment Form
-
The Importance of Risk Assessment and Safety Statement [ What Is, How to Conduct ]
-
Risk Assessments And Safety Statements Guidelines [ What Is, Process ]