Navigate the complexities of IRS representation with our in-depth guide on IRS Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form. This comprehensive resource simplifies the process of granting authorization to a tax professional, enabling them to act on your behalf with the IRS. We provide valuable tips on how to accurately complete the form and strategically use it for tax-related matters. Our guide, enriched with SEO-friendly and NLP-compatible content, is designed to enhance your understanding, ensuring that IRS Form 2848 is used effectively and to its full potential for your tax needs.
What is IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form?
IRS Form 2848, the Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative, is a document used by taxpayers to authorize an individual, usually a tax professional, to represent them before the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This form allows the appointed person to receive confidential tax information and to perform actions such as negotiating and signing agreements with the IRS on the taxpayer’s behalf. It’s specifically used for tax matters, ensuring that taxpayers can have qualified representation in their interactions with the IRS.
What is the Best Sample IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney?
Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative
Taxpayer Information:
Name: ___________________________
Identification Number (SSN or EIN): ___________________________
Address: ___________________________
Phone: ___________________________
Representative(s) Information:
Name: ___________________________
Cafeteria Number: ___________________________
Address: ___________________________
Phone: ___________________________
Tax Form:
(Form number, e.g., 1040, 941) ___________________________
Tax Type:
(e.g., Income, Employment) ___________________________
Year(s) or Period(s):
___________________________
Specific Use Not Recorded on Centralized Authorization File (CAF):
Acts Authorized:
(Detail specific powers granted)
Signature of Taxpayer:
___________________________
Date:
___________________________
Signature of Representative:
___________________________
Date: ___________________________
Declaration of Representative:
(Representative affirms their eligibility to practice before the IRS)
Note:
This is a basic template of IRS Form 2848. For actual use, it is important to refer to the official IRS Form 2848, available on the IRS website, and consult with a tax professional or legal advisor to ensure accurate completion and compliance with IRS requirements.
1. IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form and Declaration of Representative

2. IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Forms
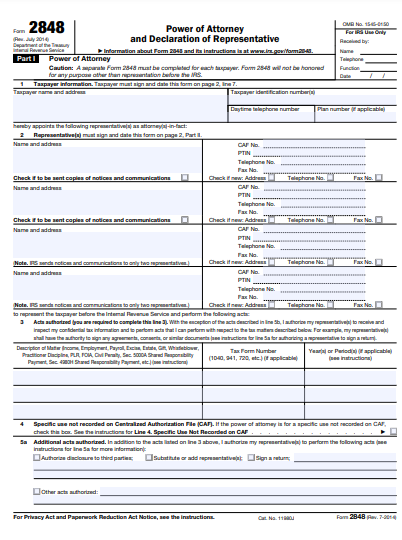
3. Texas IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Forms
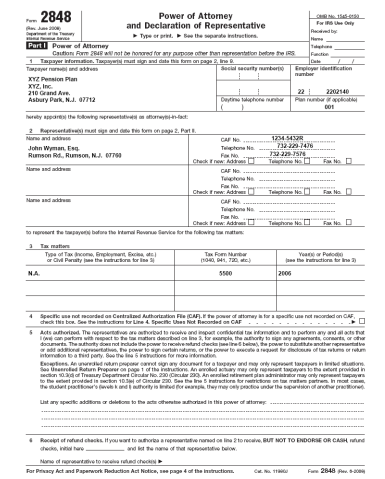
4. Printable IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

5. IRS gov / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

6. Blank IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

7. Massachusetts IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form
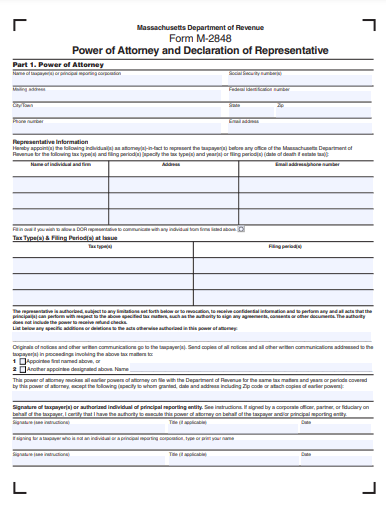
8. Simple IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

9. Ohio IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form
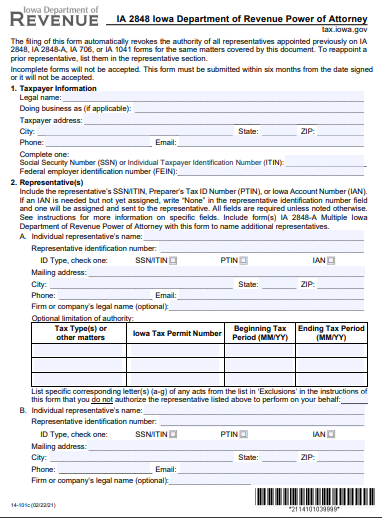
10. Durable IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

11. IRS / Form 2848 Power of Attorney Form

How do I submit Power of Attorney to IRS?
To submit a Power of Attorney (POA) to the IRS, typically Form 2848:
Related Posts
-
10+ Free New Hampshire (NH) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nevada (NV) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Nebraska (NE) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Montana (MT) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Missouri (MO) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Minnesota (MN) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Mississippi (MS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Massachusetts (MA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maryland (MD) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Maine (ME) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Louisiana (LA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kentucky (KY) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Kansas (KS) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Iowa (IA) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips
-
10+ Free Indiana (IN) Power of Attorney Form Download – How to Create Guide, Tips